The Italian explorer Christopher Columbus sailed passed the island’s east coast shores on a Sunday, November 3, 1493. Unable to make landing, he never set foot on the island but he gave the name Dominica after Dominigo for Sunday.
As was the case with the rest of the Caribbean, Dominica was already inhabited by the native Kalinago people, who used the name Wait’tukubuli meaning ‘Tall is her body”. The Kalinago (previously known as the Carib Indians) had settled on the island from around 1000AD.
Following the European’s arrival, the island remained a neutral territory for many years, serving as a refueling for ships. At this time there was much trading between the Europeans and Kaliango.
During the 1700’s the British and the French fought several times over control of the island before the British gained control in the early 1800s. The island gained independence from Britain in 1978.
Below is a brief timeline of important events in Dominica’s history.
Brief Historical Timeline
Either scroll through the timeline below or click on the toggle for a quick view for a glimpse into the events that have shaped Dominica’s environment and culture. Courtesy Lennox Honychurch.
Historical Timeline Toggle - click to open
Related Links
The Roseau Cathedral
A History of Pirates in Dominica
Mas Domnik: A History of Dominica’s Carnival
History of Sports in Dominica (olympics,, cricket..)
A History of Villages of Dominica (calibishei etc)



Historical Sites, Structures, Routes and Trails
There a number of old trails and routes which remain in use or are accessible.
Routes and Trails
- Chemin L’etang
used to reach east coast
- Jack’s walk
used by the then Governor’s son as a route up to Morne Bruce.
- WNT – segment 1?
- Jaco Flat / Steps
A hauntingly beautiful hike, used by the Maroons to get to camp
Buildings and Ruins
- Vena’s Guesthouse
Once the residence of Dominican author Jean Rhys
- Roseau Cathedral
An architectural monument in Roseau – regardless of one’s beliefs, this building has a fascinating story to tell
- Old Mill cultural center and Museam
Now the offices for the cultural division, this was the main mill for Canefield Estate.
- Bois Cotlette Estate
An old French estate house in the south of the island
- Rosalie Estate
On the east coast, near Rosalie Bay Resort, the remnants of the old watermill of what was once a large estate.
- Hillsborough Estate
Ruins seen along the Layou River, this was once one of the largest estates on the island.
- Grandbay Catholic Church
One of the oldest on the island
- Hampstead Estate
On the northeast coast, the ruins from the estate can be seen along the roadside, when approaching Hampstead River.
Sites and Scenes
- Scott’s Head
Southern most battery overlooking Soufriere Bay. Breathtaking views up the coast and across the channel.
- Morne Bruce
Battery overlooking Roseau, great way to see the city.
- French Quarter – Roseau
Walk around the oldest part of Roseau and view the various historic buildings
- Cabrits National Park
Newly restored Fort Shirley in this park overlooking Prince Rupert’s Bay and Portsmouth. Great trails to view additional ruins.
- Capuchin Battery
An old battery with breathtaking views towards Guadeloupe and the Saintes. This is the also the end of segment 13/ beginning of segment 14
Historical Sites and Structures
Bayport Residence Inn
Big Banana Campground
Caribbean Sea View Apartments
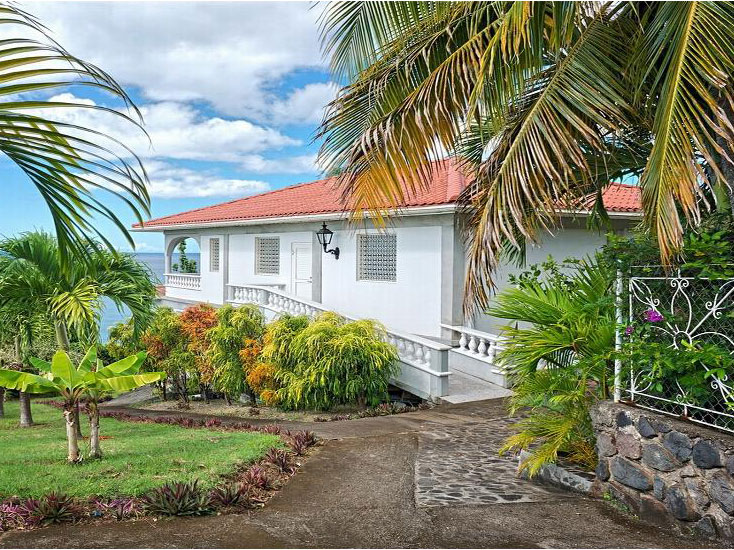

Fort Shirley Venue and Rooms
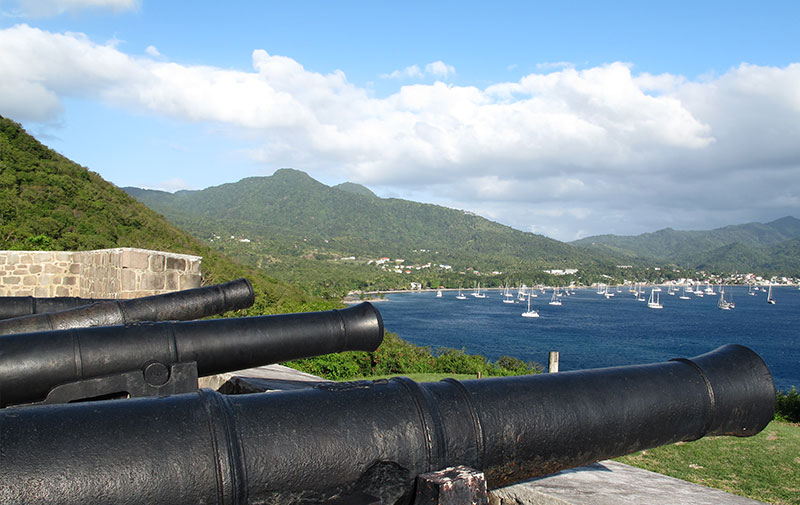

Narakiels Inn
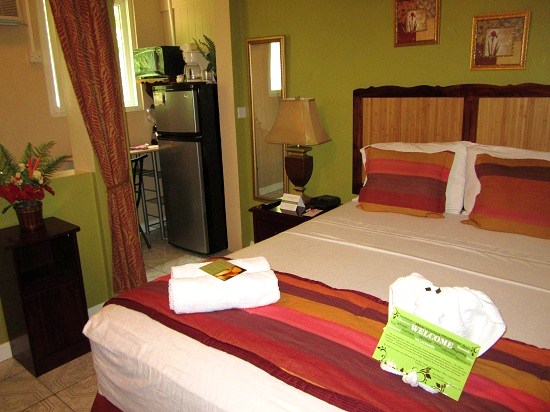

Pointe Dubique Bed & Breakfast
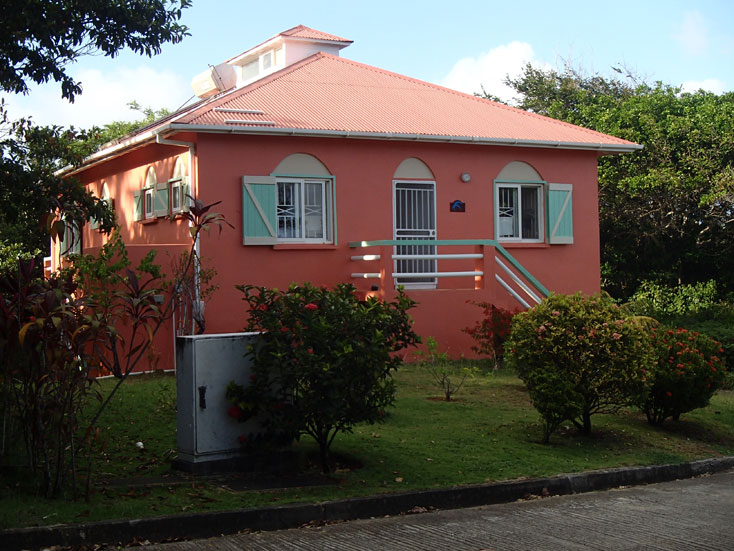

Barbwire Bar & Bungalows
Birdwatchers Rainforest Cottage
Bon Marche
Brandy Manor Guest House and Campground
Brian’s Apartment
Calibishie Gardens
Camping Zion View
Castille Paradise
Chez La Doudou Guest House
Classique International Guest House
D Smart Farm
Dominica’s Sea View Apartments
Dominique’s Hideaway
Douglas Guest House
Fingers Photo & Videography
Firefly Cottage
Freshwater Lake Kayaking
Harmony Gardens Herbal Farm
Hibiscus House
Hibiscus Valley Tours
Hodge’s View Cottage
Island Bay Boutique Hotel
Jacko Cottage
Jireh Celestial Apartment
L&O Guest House
Le Petit Paradis
Lima Ridge Cottages
Ma Bass Central Guest House
Mango Garden Cottages
My Local Secret Guesthouse
Natty Tropical Valley Cottages
Natural Vibes Dominica
Pepper’s Studio Apartments – Self Catered Apartments
Pineapple Crossing Guest House
Rachelle’s Retreat
Rejens Hotel
Roxy’s Mountain Lodge
Sandbar Village Room
Sea World Guest House
Serenity Lodges Dominica
Sisters Sea Lodge
St James Guest House
St. Aimie’s Guesthouse Apartments
The Sacred Place & Wellness Spa Retreat
The Secret Garden
The Tamarind Tree Hotel
Three Rivers Eco Lodge & Camp site
Tia’s Bamboo Cottages & Hot Springs
TiPawadi Guest house
Veranda View Guest House
Wind Blow Estate
Zen Gardens Riverfront Cottages
Zion Valley Bed and Breakfast (Moses James)
Recommended Reading
More about Dominica's past